![]()
![]()
| HOME Research East China Sea CDW |
|
Influence of environmental change in the land to the marine environment in the East China Sea and the surrounding region |
| Background |
|---|
| @@Human activities extraordinary enhanced during these decades give serious
impact to the marine environments in various manners. According to development
of the economical scale, the impacts expand from coastal waters to open
ocean through the marginal seas. At present, marine environments in the
marginal seas such as the East China Sea and the Japan Sea are getting
change. It is not clear yet how much the terrestrial environments affect
them, and how the global environmental change could influence the regional
environments. @@For@example, although we have sometimes got something warning for our enviroment such as migration of giant jerry fishes, we have not achieved understandings enough to explain such natural phenomena. To know properly the various behaviors how they are maintained and fluctuated in nature is only a resolution to realize the environmerntal change. |
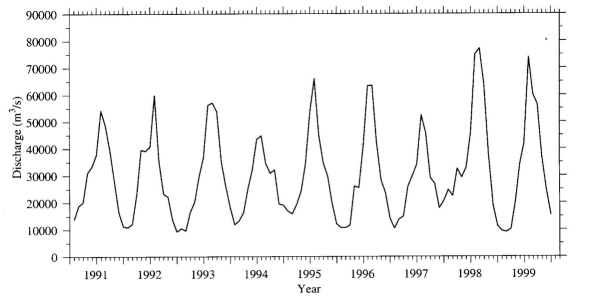 Amount of Changjiang discharge from 1991to 1999 @(From Zhu et al. 2001) |
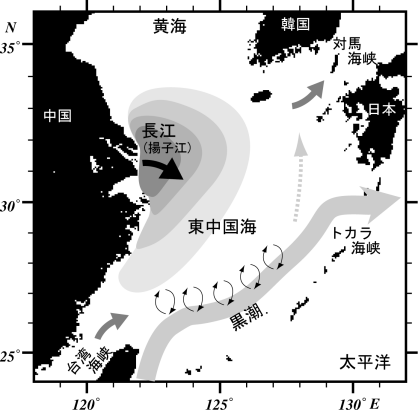 |
| We deployed satellite tracked drifters with temperature and salinity sensors in the shelf region of the East China Sea to determine the behavior of Changjiang diluted water(CDW). Movements of the drifters provide time scale of the CDW, while our observations are limited in the eastern part of the shelf region. Furthermore, temporal variation in salinity measured with the drifters could provide the information about dilution of the fresh water discharged fromthe river. Repeated observations with the drifters suggest that significant increese in salinity, namely dilution of the flesh water, could be caused by vertical mixing enhanced by strong wind such sa passage of typhoon or tropical depression. |
| Back |